What is Cannabigerol (CBG)?
What is CBG: Understanding the Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoid
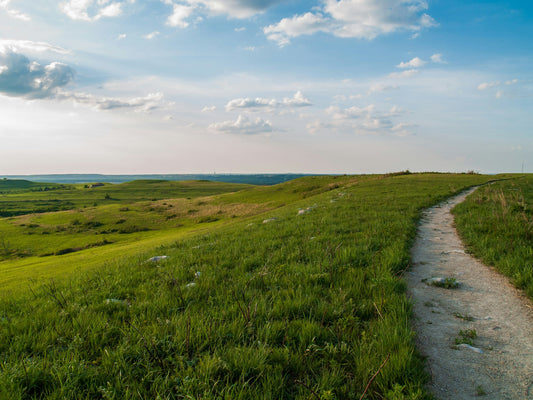
Cannabigerol, commonly referred to as CBG, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. It is a lesser-known cannabinoid compared to its more popular counterparts, THC and CBD, but is gaining attention for its potential therapeutic benefits. In this article, we will dive deeper into what CBG is, how it works in the body, and the potential therapeutic uses of this fascinating compound.
CBG: The Building Block of Other Cannabinoids
CBG is unique among the cannabinoids found in cannabis in that it is the precursor to other cannabinoids such as THC and CBD. The process begins with cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), which is present in the cannabis plant in its early stages of growth. As the plant matures, enzymes in the plant convert CBGA into various other compounds, including THC and CBD.
This means that CBG is present in lower concentrations in mature cannabis plants. In fact, it is estimated that CBG makes up only about 1% of the total cannabinoid content in most strains of cannabis. As a result, extracting CBG in high quantities can be difficult and costly, making it less available on the market. However, with advancements in breeding and cultivation techniques, growers are now able to produce higher-CBG strains, making it more accessible to consumers.
CBG and the Endocannabinoid System
CBG works by interacting with the body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is responsible for regulating various physiological processes such as appetite, pain perception, and immune function. The ECS is made up of receptors, which are found throughout the body, and endocannabinoids, which are naturally produced by the body.
CBG specifically interacts with the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS. CB1 receptors are found mostly in the brain and central nervous system, and are involved in regulating pain, mood, and appetite. CB2 receptors are found mostly in the immune system and are involved in regulating inflammation and immune response.
Therapeutic Potential of CBG
While research on CBG is still in its early stages, there has been some preliminary research into the potential therapeutic benefits of this cannabinoid. Studies have suggested that CBG may have anti-inflammatory and analgesic (pain-relieving) effects. For example, a study (British Journal of Pharmacology, 2011) found that CBG was able to reduce inflammation in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Another study (European Journal of Pain, 2011) found that CBG was able to reduce pain in a rat model of neuropathic pain.
CBG also has been studied for its potential use in treating conditions such as glaucoma, by acting as an antagonist of CB1 receptor, it can block the activity of this receptor (Neuropsychopharmacology, 2014).
Conclusion
In conclusion, CBG is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is gaining attention for its potential therapeutic benefits. Studies suggest it may have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antibacterial effects, and potential therapeutic use for conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, glaucoma, and even bacterial infections. CBG also has the potential to alleviate symptoms of stress and anxiety. However, it's important to note that research on CBG is still in its early stages, and more research is needed to fully understand its effects in humans. Despite this, the current studies and anecdotal evidence point towards the potential of CBG as a versatile and effective cannabinoid. To benefit from its potential effects, it can be consumed as an isolated compound or in combination with other cannabinoids such as CBD and THC, which can enhance its effects. It's worth consulting a doctor before starting any kind of treatment using CBG and other cannabinoids, as there could be drug interactions or side effects that need to be taken into account.